Public health stands as a cornerstone for the well-being of communities and societies. It encompasses a wide array of initiatives, policies, and practices geared towards improving and safeguarding the health of populations. But what exactly is public health, and how does it function in our society?
Exploring the Essence of Public Health
- Defining Public Health: At its core, public health refers to the science and art of preventing diseases, prolonging life, and promoting health through organized efforts at the community level.
- Focus on Prevention: Unlike clinical healthcare, which primarily deals with individual treatment, public health concentrates on preventing diseases and health issues before they occur.
- Holistic Approach: It takes a holistic approach, considering factors like environmental, social, and behavioral influences that impact health outcomes.
Key Components of Public Health
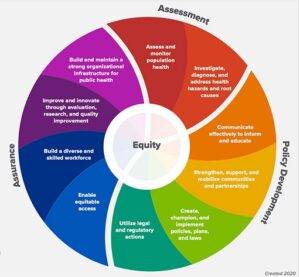
- Epidemiology: This field involves studying the patterns, causes, and effects of health and disease conditions within populations. It’s crucial for understanding and preventing the spread of diseases.
- Health Policy and Management: Public health policies and effective management strategies play a pivotal role in shaping healthcare systems, ensuring equitable access, and efficient delivery of health services.
- Environmental Health: Focusing on the impact of environmental factors on human health, this field addresses concerns such as air and water quality, food safety, and the effects of climate change.
- Social and Behavioral Sciences: Understanding human behavior in the context of health is essential for implementing effective interventions, such as promoting healthy lifestyles and disease prevention.
The Role of Public Health in Society
- Disease Prevention and Control: Public health initiatives work towards preventing the outbreak and spread of diseases, employing vaccination campaigns, sanitation improvements, and education on healthy practices.
- Health Promotion: Encouraging healthy behaviors and lifestyles through educational campaigns, awareness programs, and community engagement initiatives.
- Addressing Inequalities: A critical aspect of public health involves addressing social, economic, and health disparities to ensure everyone has equal access to healthcare services and resources.
- Emergency Preparedness: Public health plays a pivotal role in preparing for and responding to public health emergencies, such as natural disasters or disease outbreaks.
Challenges and Future Directions
- Global Health Threats: With the ever-evolving landscape of diseases and health challenges, addressing global health threats like pandemics, antimicrobial resistance, and climate change becomes paramount.
- Technology and Innovation: Embracing technological advancements and innovative solutions can revolutionize public health practices, enhancing disease surveillance, diagnosis, and treatment.
- Policy and Advocacy: Continued advocacy for policies that prioritize public health, and funding for research and initiatives, is crucial for sustained improvements in community well-being.
In essence, public health is the bedrock of our collective well-being. Understanding its multifaceted approach to preventing diseases, promoting health, and addressing societal challenges is essential. As we navigate an ever-changing world, investing in and prioritizing public health is vital for a healthier and more resilient society.


